Cantaloupe Nutrition, Benefits & How to Pick a Good Melon

Cantaloupe is a type of melon fruit that provides a range of antioxidants, phytonutrients, and electrolytes which have been shown to have multiple health benefits. The nutrients found in cantaloupe can be spotted in its deep, orange color and can help prevent oxidative stress plus a wide range of inflammatory-caused diseases that are prevalent in the US and other western nations today.
Amongst other nutrients, cantaloupe nutrition is known for containing twospecial, protective phytonutrients: carotenoids and cucurbitacins. These are two types of powerful antioxidants that have been linked with the prevention of diseases including cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders. They help to stop free radical damage within the body and to slow the aging process.
Vitamin A, found in high levels in cantaloupe, is an antioxidant known for promoting healthy vision and skin, boosting immunity, and reducing inflammation. Together with antioxidant vitamin C, which is also present in cantaloupe in high amounts, these vitamins are essential for maintaining healthy mucus membranes, celleular health, and warding off DNA damage that can lead to disease.
And there’s even more to cantaloupe’s many health benefits. Cantaloupe is now being used to extract an enzyme called superoxide dismutase (SOD). This is a strong antioxidant found mostly in the rind of cantaloupe which plays a vital role as a leading antioxidant defending the inside of human body from oxidative stress. On top of this — although they are usually discarded and only the orange flesh is eaten — cantaloupe seeds also provide important omega-3 fatty acids and are in fact edible.
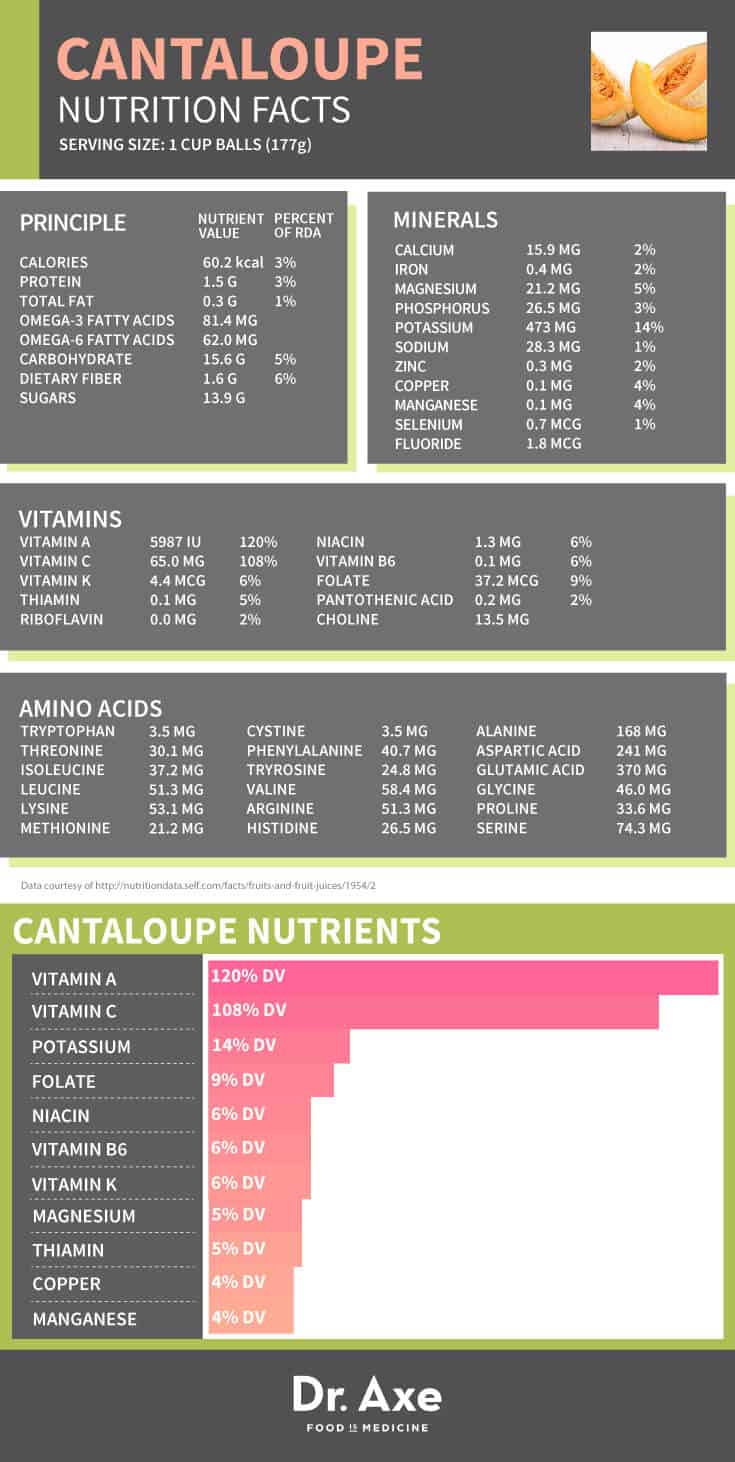
Cantaloupe Nutrition Facts
While other types of fruits like berries may have higher levels of antioxidants, cantaloupe is commonly eaten in higher volumes which can offset their lower antioxidant levels. This means that cantaloupe can in fact significantly increase beneficial levels of phytonutrients to the average person’s diet.
Cantaloupe nutrition is a great source of vitamin C and vitamin A, in the form of carotenoids. In fact cantaloupe is thought to be one of the highest fruit sources of vitamin A, while also providing potassium, and B vitamins including thiamine, niacin, folate, as well as vitamin K, magnesium, and fiber.
A one cup serving of cantaloupe contains: (1)
- 54 calories
- 0 grams fat
- 1 gram protein
- 1.5 grams fiber
- 13 grams sugar
- 13 grams carbohydrates
- 270 mg Vitamin A (120%)
- 59 mg Vitamin C (108%)
- 427 mg Potassium (14%)
- 34 mg Folate (9%)
- 1.2 mg Niacin (6%)
- 4 mg Vitamin K (6%)
- .07 mg Thiamine (6%)
- 19 mg Magnesium (5%)
12 Health Benefits of Cantaloupe

1. Great Source of AntioxidantsVitamin A and Vitamin C
Thanks to its high supply of antioxidants vitamin A and vitamin C in the form of ascorbic acid, cantaloupe nutrition helps to stop free radical damage by battling oxidative stress in the body.(2) According to research, disease prevention is one major public health benefit that can be achieved by increasing consumption of carotenoid-rich fruits and vegetables, including cantaloupe. (3)
Cantaloupe contains two types of vitamin A antioxidants called beta-carotene and alpha-carotene. And because it contains both of these carotenoids, it also contains some of their derivatives including lutein, beta-cryptoxanthin and zeaxanthin.
A growing body of literature exists regarding the effects of these antioxidants and other carotenoids on chronic diseases in humans, especially related to how they can reduce dangerous inflammation. Inflammation and free radical damage are tied to the formation of various diseases, therefore consuming cantaloupe is an excellent way to build the body’s defense against age-related conditions and to keep the body feeling young and healthy.

2. Fights Cancer with Powerful Phytochemicals
Cantaloupe is a rich source of antioxidant flavonoids such as beta-carotene, lutein, zea-xanthin and cryptoxanthin. These antioxidants have a protective role in the body and the ability to protect cells and other structures from DNA damage and stresses caused by free radicals. For this reason, studies have shown that cantaloupe can be useful in preventing colon, prostate, breast, endometrial, lung, and pancreatic cancer.
Studies show that cantaloupe’s antioxidants and cucurbitacins result in cancerous cell apoptosis, or self-destruction of the cancerous cells. These helpful chemical pheromones exist naturally in plants in order to protect the plants from external damage, but they also do the same within the human body. Cucurbitacins for example repeatedly show anti-cancer activities within the body when studied, ranging from anti-proliferation, cell cycle arrest, and cell apoptosis.
It’s believed that these compounds have apoptotic effects because they are able to enter the nuclear of the cell where the DNA or genes are stored and to activate apoptotic proteins that destroy harmful cells. (4)(5)
Additionally, many other studies have shown that consuming high amounts of fruit and vegetable sources that are naturally rich in vitamin A and vitamin C is one of the best ways to prevent cell mutation. Including 5 or more fruits and vegetables in your diet everyday can help protect from lung, colon, prostate, and oral cavity cancers because of these positive protective effects.
3. Contains Anti-inflammatory Properties
Studies have shown that in experiments lower levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) are present within the bloodstream of people who have particularly high intakes of cantaloupe and other fruits. Since CRP is a marker widely used to assess levels of inflammation in the body, this shows positive results for cantaloupe stopping dangerous inflammation and autoimmune responses that can lead to disease.
The anti-inflammatory benefits of cantaloupe nutrition stem back to its cucurbitacins, including cucurbitacin B and cucurbitacin E. These are two known anti-inflammatory compounds which can effectively alleviate pain and symptoms caused by inflammatory diseases.(6)
4. May Help Prevent Heart Disease
Heart disease, including atherosclerosis, is often attributed to high levels of inflammation as one of the leading causes. Many heart-related problems like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and a risk for heart attack or stroke start out with chronic unwanted inflammation and chronic oxidative stress. Cantaloupe nutrition’s cucurbitacins may prove useful in the treatment of different forms of heart disease because of their anti-inflammatory abilities
The most significant mechanisms with regard to cantaloupe’s anti-inflammatory abilities can be found in the fruit’s roots and rind. In fact plants belonging to these Cucurbitaceae species, which cantaloupe does, have been used as folk medicines in some countries for hundreds of years because of their wide spectrum of pharmacological activities such as reducing inflammation and the risk for heart disease and cancer.(7)
5. Boosts Immunity
The carotenes and antioxidants found in cantaloupe help to boost the immune system and to prevent infections. (8)
One specific carotenoid, beta-carotene, is especially known for boosting immunity and other chronic diseases. Studies suggest that beta-carotene may enhance immune cell function and this is the reason why it is so useful in combatting not only common illnesses, but serious conditions like cancer too. (9)

6. Helps Muscle Recovery & Stamina
Cantaloupe offers a moderate amount of the electrolyte potassium, with about 14% of your daily needs in very cup. Potassium is an important component of cell and body fluids. It helps to control a normal heart rate and to regulate healthy blood pressure. It also offers protection against heart disease, stroke, and other problems because of its importance in regulating heart and cell function.
Additionally, the potassium found in cantaloupe is an important nutrient for athletes or those who are especially active. Potassium is considered a vasodilator because it releases the tension of blood vessels and helps increase blood flow. This allows for quicker muscle recovery and reduced stress on the body as you build muscle, strength and endurance.
7. Protects Eye Health
Cantaloupe nutrition supplies important nutrients that play a vital role in protecting eye health including beta carotene, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, lutein, and zeaxanthin.
Zea-xanthin for example is an important carotenoid that is absorbed into the eye’s retinal where it is thought to provide antioxidant and protective UV light-filtering functions. And other studies show that carotenoids help to retard some of the destructive processes in the retina and the retinal pigment lining which lead to age-related macular degeneration.(10)
Since numerous studies have shown that a serious vitamin A or vitamin C deficiency can lead to glaucoma and macular degeneration, or a thickening of the cornea, and even eventually even to blindness, cantaloupe is a great way to prevent such disorders from developing.

8. Protects Skin Health
Orange colored foods, including carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin and of course cantaloupe, are also high sources of cartenoids which can reduce skin cancer risk. They are also useful of relieving pain and damage associated with sunburns and preventing signs of aging on the skin including fine lines, discoloration, and wrinkles.
9. Good for Digestion
Cantaloupe is an especially hydrating fruit, very high in water, as most types of melon are. Cantaloupe is made up of a high percentage of water, which the digestive tract needs to stay hydrated, to detoxify the body, and to properly expel toxins and waste out gut. Cantaloupe is also known to be easy on digestion and is free of FODMAPs, which are difficult to digest carbohydrates that can trigger symptoms related to Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and other digestive disorders.
10. Helps the Body to Detox
Cantaloupe nutrition is again rich with electrolytes which also help the body to detox and rid itself of excess water and fluids. This is helpful in relieving uncomfortable symptoms of bad digestion including bloating and swelling. Potassium acts as an electrolyte and promotes blow flow and hydration levels within the body, and allows oxygen to reach your cells. At the same time, it’s useful in balancing water retention in the gut and keeping you from becoming dehydrated, which can stop cases of diarrhea.
11. Restores the Body’s pH Level
Additionally melon varieties, including cantaloupe, are considered to be alkaline foods. This means they are able to help bring the pH level of the body back to its natural level. It’s believed that disease has a much harder time developing in an alkaline environment inside the body, compared to a more acidic system, so eating cantaloupe and other alkaline-forming foods can protect your body from inflammation and disease formation.
12. Low in Calories and Help Support Weight Loss
Cantaloupe contains only 60 calories per cup and is high in water and various nutrients, making a great addition to any weight loss plan. Cantaloupe is a food with a high nutrient density based on the low amount of calories it has, but the high amounts of health benefits it offers overall.
Since those following a low calorie diet can sometimes experience nutrient deficiencies, poor digestion, low immunity, and weakness, adding cantaloupe to your diet can help to balance these risks and ensure you’re acquiring plenty of vitamins and minerals in the process of losing weight.


History of Cantaloupe
Cantaloupe is a member of the Cucurbitaceae or gourd family. Some of the other popular fruits and vegetables that below to this family include winter squash, pumpkin, cucumber, and gourds.
You can see a common theme among many of these plants in that they have a deep orange or yellow color, which is an indication of their antioxidants, especially beta carotene. Cantaloupes are also of course a part of the melon family and are related to other plants including watermelon and honeydew melon.
Cantaloupe, like other melons, grows on the ground in a vine that never moves far off the surface of the dirt. It’s believed that cantaloupes first began to grow as an offspring of other related melon varieties that were native to parts of Africa. The types of melons known to be native to Africa also have relative plant species that have come from parts of Asia, including India or China, so it is not entirely known by researchers where cantaloupe first appeared.
According to historical record, cantaloupe were first reported in the northern most part of Africa along the water, where they then moved up to the south shores of the Mediterranean nations. Cantaloupe have been enjoyed by people living in the Mediterranean and Middle East region for hundreds of years and are still used in many recipes in those areas today
Today, nations including China, Turkey, Iran and Egypt are some of the major worldwide growers of cantaloupe, as is the United States. China is by far the leading producer and is thought to grow half of the world’s melons. Within the U.S., California grows the largest amount of cantaloupe, providing the country with over half of its melons every year. Other states that grow cantaloupe include Arizona, Colorado, Georgia, Indiana, and Texas
Although cantaloupe is loved most for it sweet, soft insides, there are parts of the world where cantaloupe is just as popular for its seeds. Cantaloupe seeds are dried and consumed as snacks in parts of Central and South America, as well as in Asia and the Middle East.

How to Pick a Good Melon
Melons, including watermelon and honeydew, are seasonally summer fruits, with their peak season in North America being between April through August each year. However they can commonly be found throughout most of the year, due to being grown in parts of the world where the climate is always warm.
There are two common varieties of cantaloupe that are sold and eaten most around the world: the European cantaloupe (Cucumis melo cantalupensis) which derives its name from the Italian papal village of “Cantalup”, and secondly the North American cantaloupe. The European cantaloupe is more green than orange, while the North American kind is the type usually sold in the US which has a deep orange color. Although it’s known as “cantaloupe” throughout the U.S, many other nations refer to it as “muskmelon”.
There are many different types of hybrid cantaloupe melons that exist around the world in different marketplaces which combine elements from the two most popular varieties mentioned above. Because of this, cantaloupe can be found in many different sizes, colors, and tastes.
In order to judge ripeness and taste of cantaloupe you can look for a few things:
- Without cracking into it, pick up the melon and check out its skin. You want to avoid one with many cracks and big spots of discoloration.
- Looks under the webbing of the cantaloupe and see if there is any color coming through the webbing. For regular orange cantaloupes, avoid white look skin under the web-like texture on the surface.
- Look for one that feels heavy for its size and that has a clean rind. Weight means it has a better sugar and water content, which usually means a richer and sweeter fruit.
- Try the thump test…hold the melon in one hand off any surface and thump it or flick it with your fingers (you can also tap it with your knuckle). If it sounds like it echoed or sounded a little hollow, then that’s a good sign!
- Fresh fruit should smell like the fruit. Smell the skin or stem-side of the melon and make sure it smells like the fruit. It should have a subtle warm, sweet smell.
At home, first wash the whole fruit in cold running water to get rid of dirt and potential bacteria. Most people skip this step, but it can be important to do before cutting into the fruit. Depending upon the way you want to use the cantaloupe and the size you desire, you can either cut cantaloupe into slices, cube it, or use an ice cream scoop or spoon to cut the cantaloupe into balls.
Before cutting the melon you can simply store cantaloupes in a cool, well-ventilated place like the refrigerator or on your counter. However, once you cut into the cantaloupe, sections should be kept inside the refrigerator to prevent them from going bad or developing harmful salmonella bacteria. It’s best to avoid buying and consuming cantaloupes with visible cracks and cuts for this reason, since bacteria can easily thrive there.
Using Cantaloupe in Recipes
Fresh cantaloupe can be used in many different ways: in smoothies, on top of an arugula salad, made into a spreadable jam, as part of a summer gazpacho soup, in gelato, or in homemade sorbet! There are so many ways to take advantage of its natural sweet warm flavor.
Traditionally in Italy, it is eaten along with prosciutto; however, since I do not recommend eating pork, try wrapping melon slices with beef bacon and grill it for a few minutes on each side to cook the beef bacon and bring out the juicy natural sugar of the melon. Serve your grilled melon on a salad or as a delicious BBQ side dish!
Try using cantaloupe in some of these recipes:
Cold Melon Berry Soup
Total Time: 35 minutes
Serves: 4
INGREDIENTS:
- 3 medium cantaloupes
- ¼ cup fresh lemon or lime juice
- ½ cup fresh blueberries
- ½ cup fresh strawberry
DIRECTIONS:
- Remove the peel and slice the melon into large chunks.
- Puree melon in a blender or food processor until it has liquified.
- Gently mix in lemon or lime juice and chill the mixture in the freezer for 20 – 30 minutes.
- Serve in individual bowls, garnished with fresh berries.


No comments:
Post a Comment